Use of social media in fitness centers in Spain
Uso de los Medios Sociales en los centros Fitness en España
Manel Valcarce-Torrente, Alejandro Lara-Bocanegra, Ainara Bernal-García, Fernando Pérez-Tur
Use of social media in fitness centers in Spain
Cultura, Ciencia y Deporte, vol. 19, no. 60, 2024, https://doi.org/10.12800/ccd.v19i60.2146
Universidad Católica San Antonio de Murcia
Received: 30 november 2023
Accepted: 23 february 2024
Abstract: The fitness industry in Spain is experiencing steady growth and is on the rise, relying on digitalization and social media as a basis for its continuous progression. The objective of this study was to analyze the presence of social media (web and social networks) in fitness centers in Spain during 2022, in order to understand how companies in the sector take advantage of digital platforms to interact and engage with their clients. The sample consisted of 168 chains/centers that met the previous selection criteria. Web presence, adoption of social networks, and the level of engagement achieved by fitness companies in the country were examined. The results reveal that fitness companies continue to actively use digital platforms to promote their services and establish direct communication with their audience. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that the use of the web and social networks continues to be crucial in the fitness industry. This study will enable fitness professionals to understand how companies leverage digital platforms to reach and engage their audience in an ever-changing environment.
Keywords: Web use, social networks, fitness, engagement..
Resumen: El sector del fitness en España está experimentando un crecimiento constante y se encuentra en auge, apoyándose en la digitalización y los medios sociales como base para sustentar su continua progresión. Este estudio tiene como objetivo analizar la presencia de los medios sociales (redes sociales y web) en los centros fitness de España durante el año 2022, con el propósito de comprender de qué manera las empresas del sector aprovechan las plataformas digitales para interactuar y comprometer a sus clientes. La muestra estuvo compuesta por 168 cadenas/centros que cumplían las características previas de selección. Se examinó la presencia web, la adopción de redes sociales y el nivel de engagement alcanzado por las empresas del fitness en dicho país. Los resultados revelan que las empresas del fitness continúan utilizando activamente las plataformas digitales con el fin de promover sus servicios y establecer una comunicación directa con su audiencia. En conclusión, este estudio demuestra que el uso de la web y las redes sociales continúa siendo crucial en la industria del fitness. Este estudio permitirá a los profesionales del fitness a comprender cómo las empresas aprovechan las plataformas digitales para alcanzar y comprometer a su audiencia en un entorno en constante cambio.
Palabras clave: Uso web, redes sociales, fitness, engagement.
Introduction
Currently, society is immersed in a post-digital era, where social networks have become an essential part of personal, social, and professional life for the population, even influencing the way of communicating and socializing (Escamilla-Fajardo et al., 2021; Escaño, 2019). In this context, the development and implementation of various social networks such as Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, and TikTok have created spaces that allow more specific interactions with people, the creation of groups, sending messages, and the production and consumption of content (Gil-Quintana et al., 2022). These social networks have caused a true revolution in the way human beings communicate and socialize (Escamilla-Fajardo et al., 2021). Moreover, demographic data support this statement, since out of the 8,010 billion inhabitants in the world, approximately 5,440 billion use mobile devices, 5,160 billion have access to the internet, and nearly 60% of the global population (equivalent to 4,760 billion people) are active social media users (Meltwater & WeAreSocial, 2023). These figures confirm that social networks have currently become an integral part of people's lives.
On a national level, 85% of Spain's population (28,3 million people) are social media users, with women (52%) having a slightly higher percentage than men (48%) (IAB Spain & Elogia, 2023). Additionally, Meltwater and WeAreSocial (2023) indicated that the top-5 most used social networks in Spain were: WhatsApp, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and TikTok. Furthermore, the national population spends an average of 67 minutes using social networks, with mobile use dominating for consumption (97%) (IAB Spain & Elogia, 2023). Clearly, the sports sector could not remain isolated from this trend of growth and digitalization. In this regard, sports organizations have recognized the potential of digitalization to improve performance and are investing in creating solid digital foundations and emerging technologies (Deloitte, 2023). In recent years, digitalization has been implemented quickly and precisely in the sports field, and more specifically in fitness centers, largely related to the Covid-19 pandemic and the need to continue working, being in contact with clients, optimizing time, etc. (Amankwah-Amoah, 2021; García-Fernández et al., 2022, Núñez-Sánchez et al., 2020). Similarly, this sector at the national level is highly consolidated, with more than 60 operators and about 4,000 centers, presenting one of the highest penetration rates in Europe (Gálvez-Ruiz et al., 2023).
On the other hand, there are various studies that highlight the benefits of using social networks in the fitness sector (Conrad & Allen, 2013), demonstrating their usefulness for various functions and interaction with clients. An example of this is the use of Facebook and Instagram platforms by the marketing departments of fitness centers, which allows establishing direct contact with users, using friendly language, comparing their progress, etc. (Kim, 2022; Valcarce-Torrente et al., 2021; Wright et al., 2017). Other authors consider that social networks are one of the most valuable management tools used by sports managers in their daily work (López-Carril et al., 2021). From the user's perspective, there is a trend among young people to seek inspiration from influential individuals in matters of health and lifestyle through social networks (Lim et al., 2022). In this sense, Kim (2022) indicates that there should be an encouragement to compare fitness abilities with those of artists and/or role models to follow, since motivation within physical activity infers a direct and positive effect on participation in the activity itself.
Likewise, the organizations themselves are investing in technology, as digital innovation is expected to drive the emergence of new business models, creating multiple revenue opportunities (Deloitte, 2023). Gálvez-Ruiz et al. (2023) highlight the importance of new technologies in this sector and advocate for their deeper analysis and study. Everything mentioned above underscores the importance of analyzing and understanding the impact of social networks in the field of fitness, which will allow for an understanding of the use of the web and social networks by fitness centers, identifying the most used platforms in the sector, analyzing engagement, and making comparisons with previous data. In this regard, it should be noted that engagement is a multidimensional concept that encompasses the thoughts, emotions, and behaviors of consumers towards a company (Behnam et al., 2021). As Behnam et al. (2021) point out, engagement acquires added importance for fitness centers because it acts as a key antecedent to consumer behavioral loyalty. In addition, various authors have highlighted the importance of engagement, determining that service experience influences consumer commitment through satisfaction and emotional attachment, as well as engagement can be a stimulus for co-creation (Behnam et al., 2021; Hollebeek et al., 2019; Kumar et al., 2019). The fitness sector in Spain is experiencing steady growth and is booming. Supported by the current trend of digitalization and social networks, it could sustain its continuous progression, generating benefits for both organizations and the general population, and having a positive impact on people's health.
The present study's primary objective is to analyze the presence of social media in companies of the sector, assessing the availability and functionality of their corporate pages. The second objective is to examine their adoption of social networks such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, Twitter, and TikTok. Furthermore, the concept of engagement and its measurement in the context of social networks are explored. The different strategies used by Fitness centers to promote interaction and participation of users on these platforms are analyzed, and how they have evolved compared to previous years.
Materials and Methods
The presented study is quantitative, descriptive, and cross-sectional in nature. These methodological decisions have been made based on the proposed research objectives. These characteristics allow for a snapshot of the situation or characteristics of the analyzed entities at a specific moment and to analyze the data in an objective and quantitative manner.
Participants
To achieve the proposed objectives, an analysis was conducted on companies listed under the CNAE code 9313: Activities of gyms, and companies with the highest turnover registered under the CNAE code 9311: Management of sports facilities, according to data obtained via the SABI platform.
The inclusion criteria for the analysis of companies from both registries were: having a minimum of five employees, operating in Spain, belonging to the fitness center sector, and being active (not in the process of dissolution, liquidation, or extinction). Additionally, from the companies under the CNAE code 9311, the top ten companies in the sector with the highest turnover were accounted for. Likewise, companies that belonged to the same fitness center chain were unified.
From the data obtained in SABI and after applying the selection criteria, the sample subject to analysis resulted in 168 companies.
The collection of descriptive data was carried out over 10 days between December 21 and 31, 2022 (inclusive).
Given that on several occasions the fiscal name shown in the SABI database does not match the commercial name of the companies to be analyzed, it was necessary to consult their websites, contact company directors and/or those responsible, and use different specialized sector pages where information could be gathered.
Various social media were analyzed, including the use of the web (corporate web page) as well as the social networks of each of the fitness chains/centers. Once the analysis was completed, the total number of social networks used by these companies was analyzed, and the most used social networks in the sector were identified. All collected data were added to an observation template composed of each of the necessary factors for subsequent analysis.
Instruments
To perform the analysis of the engagement of those chains/centers that had a corporate profile in the most used social networks, the following instruments were used:
The measure of Oviedo-García et al. (2014) and recently adapted in the fitness sector by García-Fernández et al. (2017):
-
Engagement on Facebook = (Likes + Comments + Shares) / (Number of Posts)
Likewise, the latter formula has also been adapted for its use on Twitter and Instagram:
-
Engagement on Twitter = (Favorites + Mentions + Retweets) / (Number of Tweets)
-
Engagement on Instagram = (Likes + Comments) / (Number of Posts)
The proposal by Rival IQ, a specialist in digital activities and competitive analysis:
-
Total Engagement on Facebook = (Likes + Comments + Shares) / (Number of Posts)
-
Total Engagement on Twitter = (Favorites + Retweets) / (Number of Tweets)
-
Total Engagement on Instagram = (Likes + Comments) / (Number of Posts)
The measure proposed by Social Media Management AgoraPulse and its adaptation for Instagram:
-
Total Engagement on Facebook = (Likes + Comments + Shares) / (Number of fans (total)) x 100
-
Total Engagement on Twitter = (Favorites + Retweets + Mentions) / (Number of Followers (total)) x 100
-
Total Engagement on Instagram = (Likes + Comments) / (Number of fans (total)) x 100
Procedure
The collection of descriptive data was carried out over a period of 10 days, from December 21 to 31, 2022 (both inclusive).
First, the use of the corporate website and social networks by each fitness chain or center was analyzed. Once this analysis was completed, the total number of social networks used by these companies was examined and the most popular platforms in the sector were identified. All data collected was recorded in an observation template that included the various elements necessary for further analysis.
Subsequently, the engagement of those chains or centers with a corporate profile on the most widely used social networks in the sector was assessed.
It is important to mention that, due to the complexity of social media analysis, exclusion criteria were applied to some chains or centers:
Those using a user profile as the main page instead of a fanpage on the Facebook social network, or if their profile was inaccessible, as in the case of private profiles on Twitter or Instagram.
In the case of chains, if they did not have a dedicated chain profile and instead had separate profiles for each of their centers, they were considered null. If they had a chain profile, only that profile was taken into account, excluding the rest of the profiles.
Social media networks of chains without a specific profile for their brand in Spain were not included, or in cases where it was impossible to find an official chain profile.
These criteria ensured the coherence and reliability of the data analyzed in the study.
Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, the collected data were recorded in the spreadsheet, analysis, and data visualization program Microsoft Excel.
In this program, all values related to the different profiles of the entities under analysis were recorded, including the results of evaluated items such as followers, comments, and posts. Subsequently, to fulfill the study's objectives, a descriptive analysis was performed to obtain the count of social media platforms used, and the proposed formulas were applied for calculating engagement.
Results
Analysis of the web and social media
After conducting the study of the 168 chains/centers that met the pre-selection criteria, it has been determined that 91.07% (n = 153) had their own corporate website (Table 1).
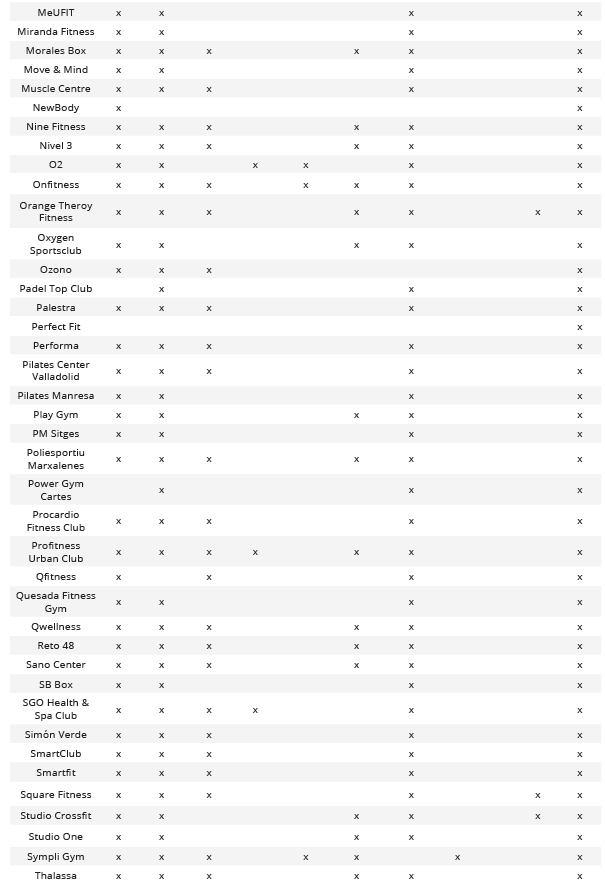
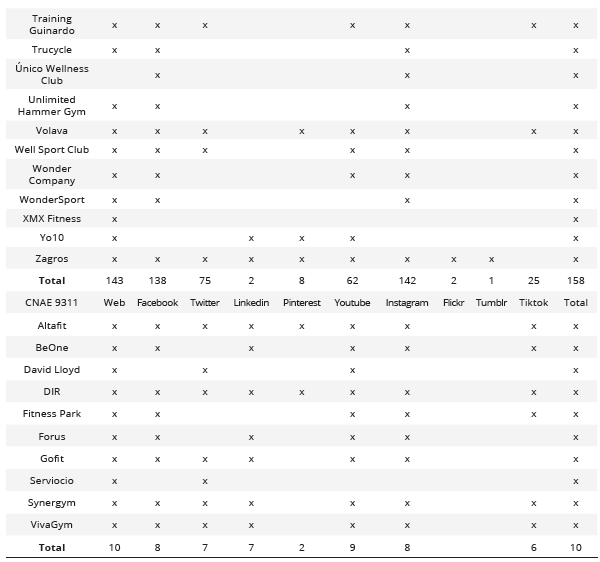
Number of social profiles by social network and the percentage it represents in relation to the total entities analyzed
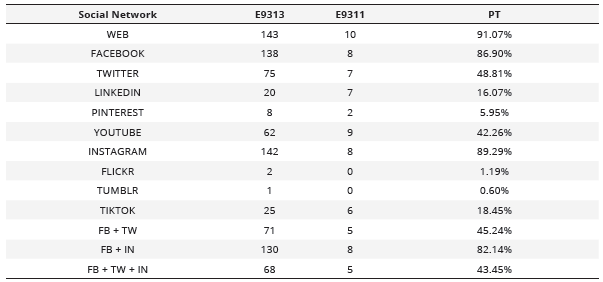
FB = Facebook; TW = Twitter; IN = Instagram; E9313 = Entities CNAE 9313; E9311 = Entities CNAE 9311; PT = Total percentage in relation to the total entities.
According to the main characteristics, the used social media platforms are classified into three main groups: Social Networks, Microblogging, and Video and Image Social Networks. Within the first group, which includes both brief and extensive posts, videos, images, chats, and messaging systems, Facebook and LinkedIn were found. Concerning the Microblogging typology, characterized by brief and simple posts, messaging systems, and links, Twitter stands out. Lastly, in the Video and Image Social Networks group, the prioritized platforms are YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok, respectively.
After analyzing each of the different social media platforms used by companies in the sector, it was determined that Facebook stands out in the Social Networks category, Twitter in the Microblogging category, and Instagram in the Video and Image Social Networks category. Finally, it was identified that up to 43.45% (n = 73) of companies in the sector had a corporate profile on the three most common social networks simultaneously (Table 2).
Relation between Social Media used by each of the entities analyzed based on CNAE 9313 and CNAE 9311
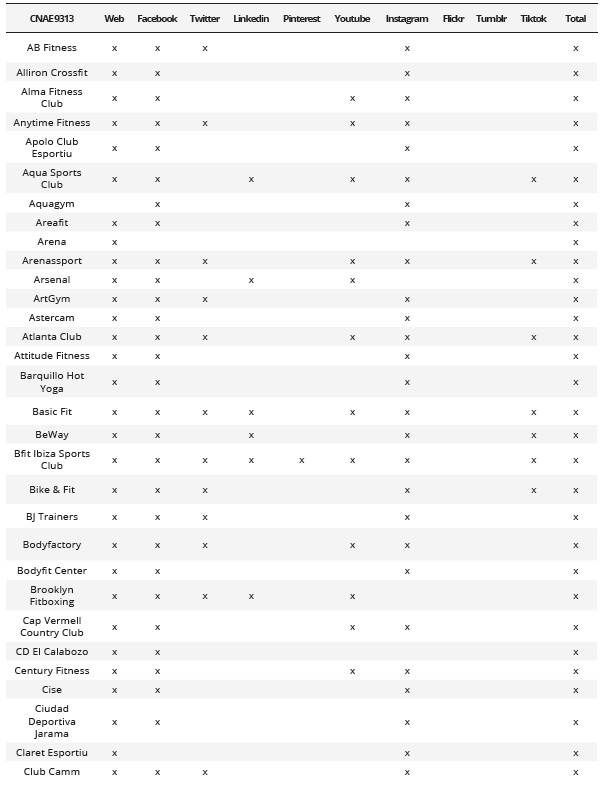
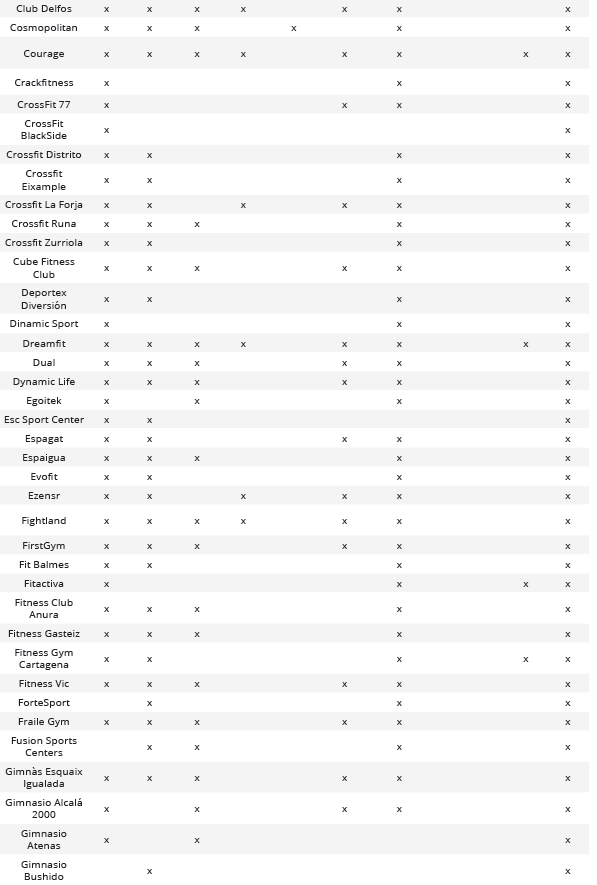
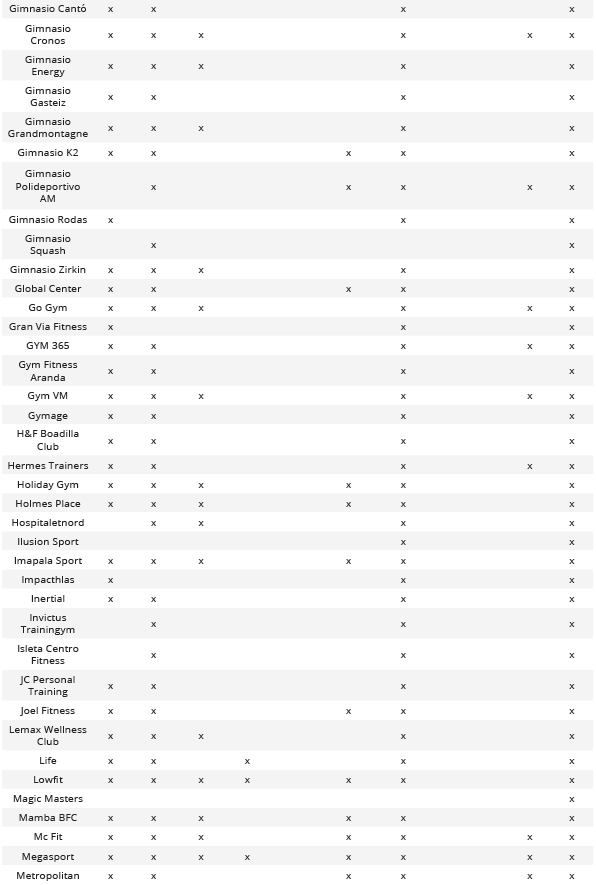
Analysis of Fans and/or Followers on the Most Used Social Media Platforms
Referring to the total number of fans and/or followers on the Facebook Fanpages or the corporate profiles of Twitter and Instagram (Table 3), it is observed that the fitness chains/centers with the highest number of followers on Facebook are: Basic Fit (1,104,918), Mc Fit (514,849), and Holmes Place (489,522).
Entities with the most followers on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram
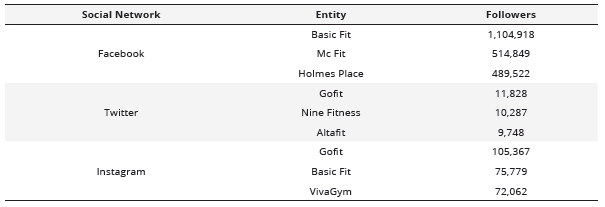
Furthermore, on Twitter, those with the highest number of followers are: Go Fit (11,828), Nine Fitness (10,287), and Altafit (9,748). Regarding Instagram, Go Fit (105,367), Basic Fit (75,779), and VivaGym (72,062) would be the companies with the highest number of followers.
Analysis of Engagement on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram
Using the measures mentioned in the methodology to evaluate Engagement, the following table presents the results obtained for each of the analyzed fitness chains/centers. It should be noted that results where the Engagement is equal to zero correspond to those social media profiles that did not undertake any activity or action during the analysis period.
On the Facebook platform (Table 4), it is observed that the companies with the highest Engagement, according to the study conducted by García-Fernández et al. (2017) and RivalIQ, are: Gofit (57.3), VivaGym (40.8), and ArenasSport (35.0). Furthermore, using the measure proposed by AgoraPulse, it was found that Training Guinardo (8.6), ArenasSport (4.5), and Simón Verde (3.1) achieved the highest Engagement.
Analysis of posts and interactions of active companies on the Facebook social network
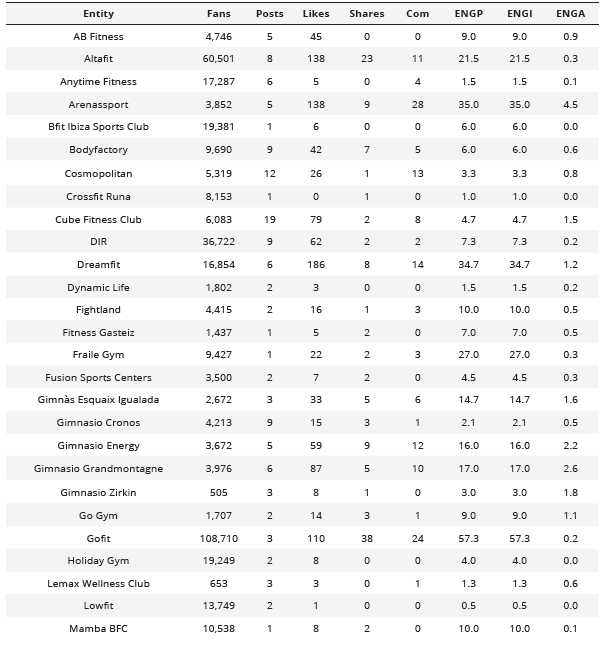
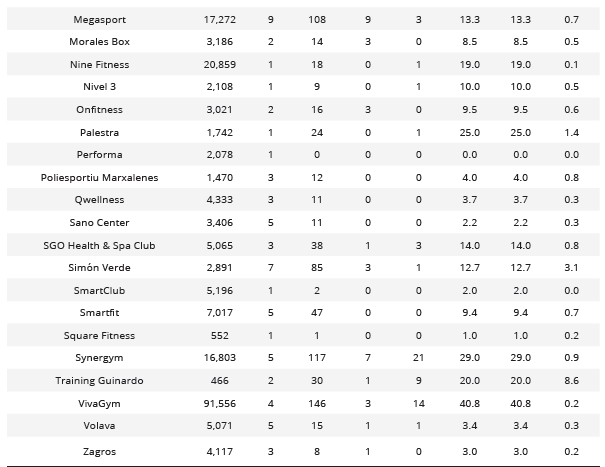
Com = Comments; ENGP = Article Engagement; ENGI = RivalIQ Engagement; ENGA = Agorapulse Engagement
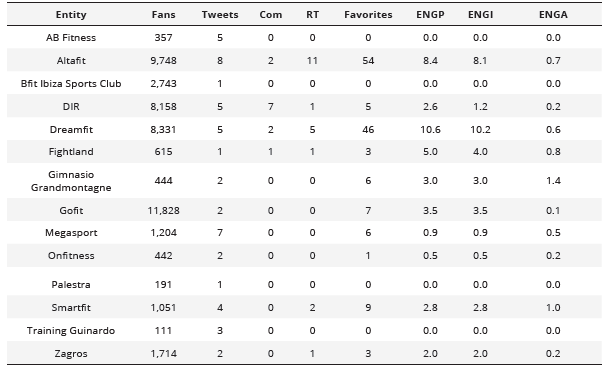
On Twitter, according to the study by García-Fernández et al. (2017) and the RivalIQ metric (Table 5), the companies with the highest engagement were identified, which are: Dreamfit (10.6 and 10.2), Altafit (8.4 and 8.1), and Fightland (5.0 and 4.0). On the other hand, using the measure proposed by AgoraPulse, it was observed that Gimnasio Grandmontagne achieved the highest engagement (1.4), followed by Smartfit (1.0), and Fightland (0.8).
Analysis of posts and interactions of active companies on the Twitter social network
Finally, on the Instagram social network (Table 6), the companies with the highest engagement are: Nine Fitness (26,237.0), Gofit (872.8), and Dreamfit (733.8) according to the measure proposed by Oviedo-García et al. (2014) and RivalIQ. Regarding the results obtained for engagement with the AgoraPulse measure; Nine Fitness (245.9), Cube Fitness Club (38.3), and Fitness Vic (24.6).
Analysis of posts and interactions of active companies on the Instagram social network
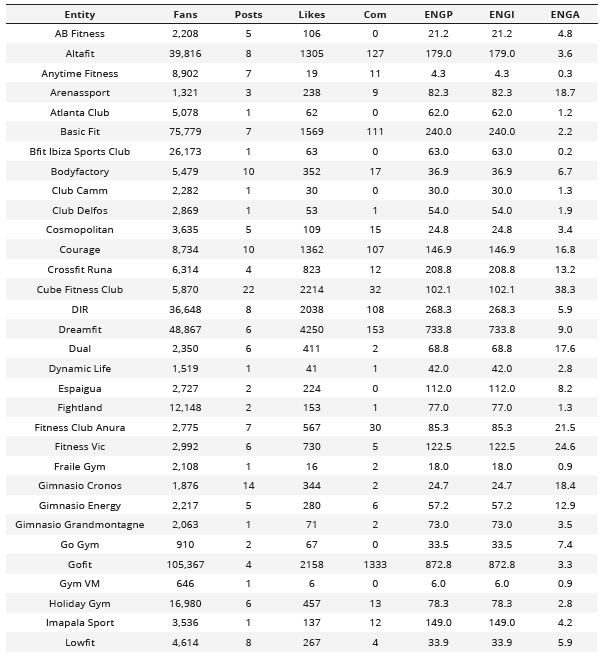
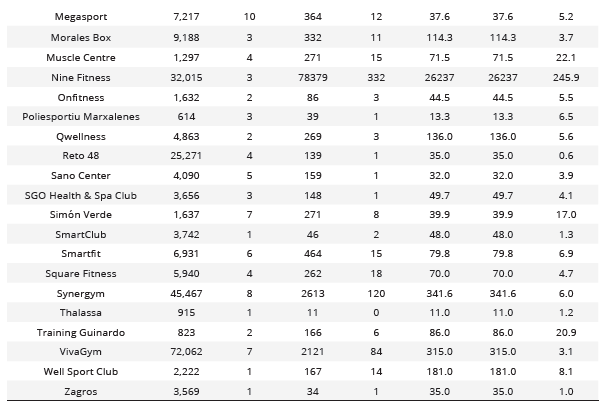
Com = Comments; ENGP = Article Engagement; ENGI = RivalIQ Engagement; ENGA = Agorapulse Engagement
It should be noted that the measure proposed by both Oviedo-García et al. (2014) and RivalIQ prioritizes directly counting the engagement of social profiles without giving importance to the number of fans/followers. Therefore, profiles with a higher number of followers could have higher Engagement as they have a larger "audience." On the other hand, AgoraPulse does take into account the number of fans/followers, showing a more direct relationship between Engagement and the available audience.
Discussion
As the world adapts to the "new normal," overcoming the health crisis, it is crucial to understand how fitness centers have utilized digital platforms to stay connected with their clients. Moreover, with society immersed in the digital era, marked by constant evolution, the use of the web and social media has become essential for businesses in the fitness industry (Deloitte, 2023; Meltwater & WeAreSocial, 2023). Thus, these platforms offer unprecedented opportunities for promotion, communication, and customer engagement.
Considering the presence on corporate websites of organizations linked to the fitness sector, this study has highlighted that just over 91% have their own website. These findings emphasize the importance the sector places on the use of new technologies and digital innovation, especially after the Covid period, which propelled its development and advancement (Amankwah-Amoah, 2021; Gálvez-Ruiz et al., 2023; García-Fernández et al., 2022).
On the social media front, it is worth noting that the analyzed fitness centers exhibit a certain trend towards the use of these channels. In this case, the results show that the most utilized social media platform in the fitness sector is Instagram, surpassing Facebook. Thus, over 82% of organizations have an account on both Facebook and Instagram, while more than 43% of the analyzed organizations have accounts on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Additionally, TikTok emerges as a rapidly growing social media platform among the younger demographic, with an increased usage by fitness centers compared to previous years (Pérez-Tur et al., 2022). The rise of TikTok is not surprising, as it directly engages with the younger audience, and even in academic settings, it has been recognized as a tool facilitating learning, communication, and education (Escamilla-Fajardo et al., 2021).
These findings align with the global social media usage data from Meltwater y WeAreSocial (2023), indicating that just under 60% of the world's population (4,76 billion people) are social media users. On a national level, individuals spend an average of 70 minutes per day using social media on their mobile phones (IAB Spain & Elogia, 2023), underscoring the significance of these platforms for both individuals and sports organizations alike.
In this regard, fitness centers have recognized that the way they communicate with their clients has shifted towards the digital realm, specifically through social media. This has led to the necessity of having a corporate presence on social media as a means of interaction and communication (Valcarce-Torrente et al., 2021). For other authors, these platforms emerge as a valuable management tool for the professional performance of sports managers (López-Carril et al., 2021).
Building upon the data related to fans/followers on the primary social media platforms of fitness centers, it should be noted that Instagram leads the list, surpassing Facebook and Twitter. These results align with those presented at a generic level for the Spanish population by Meltwater y WeAreSocial (2023). Hence, it could be argued that fitness centers are leveraging scientific insights and understanding that the methods of interaction, communication, and customer acquisition might be evolving. Valcarce-Torrente et al. (2021) have already pointed out that marketing departments are harnessing the benefits of these tools to engage in direct and tailored communication with their customers.
However, concerning the engagement data, it could be noted that it has decreased compared to previous years (Pérez-Tur et al., 2022). This is an aspect that requires further analysis; nevertheless, it could be attributed to the strategy that social media platforms are adopting to reduce organic reach, inevitably resulting in a decrease in engagement for businesses. This suggests that, despite the beneficial use of social media, continuous monitoring and updating with a professional and corporate approach are necessary. Therefore, it is understood as crucial for fitness centers to focus attention on generating that engagement with their clients, thus avoiding potential customer attrition. As Gil-Quintana et al. (2022) outlined, the development and implementation of social media are enabling the creation of more specific spaces for communication, interaction, content consumption, etc. Thus, fitness centers are leveraging the strengths of social media to support their exponential growth and social development.
Limitations
The authors of the study acknowledge and are aware of certain methodological limitations that could impact the obtained results. These limitations include:
Firstly, the lack of necessary information about some companies in the database used for the study. It is possible that some relevant companies in the sector may not be included in the analysis due to a lack of available data. This could affect the representativeness of the sample and limit the generalization of the results.
Furthermore, the authors did not have access to private statistical data that could have provided additional information on the engagement factors proposed by Oviedo-García et al. (2014), adapted by García-Fernández et al. (2017). This includes the inability to access specific interaction data, such as "stories" that are not made public, and whose impact cannot be externally quantified. This lack of access to detailed data may limit a comprehensive understanding of engagement on the studied social media platforms.
Another significant limitation is the lack of consensus and variability in the factors comprising the engagement formula across different social media platforms. Since there are multiple factors and interaction possibilities on the platforms, there is no universally accepted formula for measuring engagement. This can make direct comparisons between social media platforms challenging and may complicate the interpretation of results.
Finally, certain profiles may limit access or visibility to specific data necessary for the analysis. This could be due to privacy settings or internal decisions of the companies that restrict the availability of certain information. These limitations in data access may impact the accuracy and representativeness of the obtained results.
With the intention of mitigating some of these limitations, it is proposed that future research include an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing the decrease in engagement to establish efficient strategies. On the other hand, seeking the participation of the companies within the study sample could be considered, intending to gather information that enriches the analysis and contributes more knowledge to the sector.
Conclusions
The objectives of this present article were to analyze the online presence of companies in the fitness sector, assessing the availability and functionality of their corporate websites, examining their adoption of social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, Twitter, and TikTok, and, finally, exploring the concept of engagement and its measurement in the context of social media. Thus, different strategies used by fitness centers to encourage user interaction and participation on these platforms and their evolution over time were analyzed. Based on the results obtained, various relevant conclusions were drawn regarding the fitness center sector and its presence on social media.
Firstly, it can be concluded that the analyzed companies attach importance to having an online presence and using digital tools to promote themselves and reach a wider audience. This is supported by the fact that a vast majority, specifically 91.07% of the analyzed fitness chains and centers, have a corporate website. This demonstrates the significance these companies place on establishing an online presence.
As a second conclusion, it can be asserted that there is a shift in the use of social media by companies in the sector, as there is a clear trend towards using Instagram as the primary platform for promotion and communication with customers. For the first time, Instagram has surpassed Facebook as the most popular social media platform in the fitness industry.
On the other hand, the importance of maintaining an active presence across multiple platforms to maximize the reach and visibility of companies in the fitness sector is demonstrated, as a combined use of different social media platforms by these companies has been identified.
Similarly, it can be concluded that social media serves as communication and promotion channels for fitness sector companies. In terms of followers and engagement on social media, interesting data has been obtained. On Facebook, the average number of followers on the analyzed companies' fanpages is 12,277.06, with Basic Fit being the company with the most fans, reaching the figure of 1,104,918 followers. On Twitter, Gofit leads in the number of followers with 11,828, but only 19.18% of the companies use this platform. On the other hand, on Instagram, the average number of followers is 13,037.58, and Gofit also stands out with 105,367 followers. In terms of engagement, it is observed that Instagram achieves the highest average, followed by Facebook and Twitter. These data illustrate the importance of these social media platforms as communication and promotion channels for companies in the fitness sector.
However, a decrease in the average engagement has been identified compared to previous years (Herrera-Torres et al., 2021; Pérez-Tur et al., 2022). This indicates that companies in the sector should pay special attention to improving their social media engagement strategy.
Furthermore, it is interesting to note that TikTok is gaining ground in the fitness sector. The number of active profiles on this platform has experienced a significant increase compared to the previous year (Pérez-Tur et al., 2022). This demonstrates that companies are recognizing the potential of TikTok as a platform to reach a younger audience and generate creative and entertaining content.
In summary, the results of this study indicate that Instagram is the leading social media platform in terms of engagement for fitness chains and centers, followed by Facebook and Twitter. However, it is important to note that engagement figures may vary based on the strategies and specific content used by each company. Additionally, the growth of TikTok as a relevant platform in the fitness sector underscores the importance of adapting to emerging trends on social media to maintain an effective online presence.
The implications for management arising from this updated analysis aim to provide a detailed and current insight into the use of the web and social media in the fitness industry in Spain during the year 2022. This allows fitness professionals to understand how companies leverage digital platforms to reach and engage their audience in an ever-changing environment.
Ethics Committee Statement
This study did not involve research with human data.
Conflict of Interest Statement
There are no conflicts of interest and no entity/organization has influenced this research.
Funding
This research is part of the project titled Consolidation of the Knowledge-Based Company (EBC), Fitbe. A digital platform for the management and promotion of physical activity (AT 21_00031), funded by the Junta de Andalucía.
Authors' Contribution
Conceptualization M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Methodology M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Software M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Validation M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Formal Analysis M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Investigation M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Resources M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Data Curation M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Writing – Original Draft M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Writing – Review & Editing M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Visualization M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Supervision M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Project Administration M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T.; Funding Acquisition M.V.T., A.L.B., A.B.G & F.P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the first author of this article [manelv@valgo.es].
References
Agorapulse. (30 de diciembre de 2022). Social Media Management. https://www.agorapulse.com/es/funcionalidades/social-media-analytics/
Amankwah-Amoah, J., Khan, Z., Wood, G., & Knight, G. (2021). COVID-19 and digitalization: the great acceleration. Journal of Business Research, 136, 602-611. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.08.011
Behnam, M., Sato, M., & Baker, B. J. (2021). The role of consumer engagement in behavioral loyalty through value co-creation in fitness clubs. Sport Management Review, 24(4), 567-593. https://doi.org/10.1080/14413523.2021.1880772
Conrad, C. & Allen, L. (2013). Internet marketing for health and fitness clubs. Wakefield, RI: Communications Consultants WBS. https://www.amazon.es/Internet-Marketing-Health-Fitness-English-ebook/dp/B00HCZ5PLA
Deloitte (2023). The Future of Sport. Forces of change that will shape the sports industry by 2030.https://www2.deloitte.com/uk/en/pages/sports-business-group/articles/the-future-of-sport-march-2023.html
Escamilla-Fajardo, P., Alguacil, M., & López-Carril, S. (2021). Incorporating TikTok in higher education: pedagogical perspectives from a corporal expression sport sciences course. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 28, 100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2021.100302
Gálvez-Ruiz, P., García-Fernández, J., Gonçalves, C., & Alcaraz-Rodríguez, V. (2023). The Iberian fitness industry: experiences from Portugal and Spain. In J. García-Fernández, M. Grimaldi-Puyana, & G. A. (Ed.), Bravo Sport in the Iberian Peninsula (pp. 98-108). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003197003-9
García-Fernández, J., Elasri-Eijaberi, A., Pérez-Tur, F., Triadó-Ivern, X. M., Herrera-Torres, L., & Aparicio-Chueca, P. (2017). Social networks in fitness centres: the impact of fan engagement on annual turnover. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 17(3), 1068-1077.https://doi.org/10.7752/jpes.2017.03164
García-Fernández, J., Valcarce-Torrente, M., Gálvez-Ruiz, P. & Mohammadi, S. (2022). The challenges of digital transformation in the fitness industry in the world. In J. García-Fernández, M. Valcarce-Torrente, S. Mohammadi, & P. Gálvez-Ruiz (Ed.), The Digital Transformation of the Fitness Sector: A Global Perspective (pp. 1-3). Emerald Publishing Limited, Leeds. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80117-860-020221001
Gil-Quintana, J., Felipe-Ruiz, R., & Moreno-Muro, M. Á. (2022). Influencers deportivos y su repercusión en el consumo, la actividad física y su proyección en redes sociales por los adolescentes andaluces (España). Retos: Nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación, 43, 591-602. https://doi.org/10.47197/retos.v43i0.89518
Herrera-Torres, L., Pérez-Tur, F., Valcarce-Torrente, M., López-Carril, S., Alonso-Dos-Santos, M., & García-Fernández, J (2021). La utilización de la web y las redes sociales en la industria del fitness en España, Informe 2020. Valgo. https://www.valgo.es/6o-informe-uso-web-y-redes-sociales-en-fitness-2020
Hollebeek, L. D., Srivastava, R. K., & Chen, T. (2019). SD logic–informed customer engagement: integrative framework, revised fundamental propositions, and application to CRM. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47, 161-185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-016-0494-5
IAB Spain & Elogia (2023). Estudio de Redes Sociales 2023. Iabspain. https://iabspain.es/estudio/estudio-de-redes-sociales-2023/
Kim, H. M. (2022). Social comparison of fitness social media postings by fitness app users. Computers in Human Behavior, 131, 107204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107204
Kumar, V., Rajan, B., Gupta, S., & Pozza, I. D. (2019). Customer engagement in service. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47, 138-160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0565-2
Lim, M. S., Molenaar, A., Brennan, L., Reid, M., & McCaffrey, T. (2022). Young adults’ use of different social media platforms for health information: Insights from web-based conversations. Journal of medical Internet research, 24(1), e23656. https://doi.org/10.2196/23656
López-Carril, S., Villamón, M., & González-Serrano, M. H. (2021). Linked(In)g sport management education with the sport industry: A preliminary study. Sustainability, 13(4), 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042275
Meltwater & WeAreSocial. (2023). Digital 2023: Global Overview Report. https://www.meltwater.com/en/2023-global-digital-trends
Núñez-Sánchez, J. M., Gómez-Chacón, R., & Jambrino-Maldonado, C. (2020). Digital tools for adapting corporate wellness programmes to the new situation caused by Covid-19: a case study. In B. Sañudo-Corrales, & J. García-Fernández (Ed.), Innovation in Physical Activity and Sport (Tapasconference 2020). (pp. 74-87). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92897-1_9
Oviedo-García, M. A., Muñoz-Expósito, M., Castellanos-Verdugo, M. & Sancho-Mejías, M. (2014). Metric proposal for customer engagement in Facebook. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 8(4), 327-344.https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-05-2014-0028
Pérez-Tur, F., Valcarce-Torrente, M., López-Carril, S., Lara-Bocanegra, A. & García-Fernández, J. (2022). La utilización de la web y las redes sociales en la industria del fitness en España, Informe 2021. Sevilla: Wanceulen. https://www.valgo.es/blog/publicado-el-7o-informe-sobre-el-uso-de-la-web-y-las-redes-sociales-en-la-industria-fitness-en-espana-en-2021?elem=277600
Rival IQ: Digital Marketing Analytics (2016). Powerful social media analytics. No data scientist required. https://www.rivaliq.com/
Valcarce, M., Cordeiro, C., & Miñambres, T. (2017). Evolución y análisis de los seguidores en redes sociales de las principales cuentas de centros de fitness de España. Podium, Sport, Leisure and Tourism Review, 6(3), 14-29.https://doi.org/10.5585/podium.v6i3.224
Valcarce-Torrente, M., Gálvez-Ruiz, P. & García-Fernández, J. (2021). The Spanish Fitness Industry. In García-Fernández, J. & Gálvez-Ruiz, P. (Ed.), The Global Private Health & Fitness Business: A Marketing Perspective (págs. 15-23). Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80043-850-720211007
Williams, J., & Chinn, S. J. (2010). Meeting relationship-marketing goals through social media: A conceptual model for sport marketers. International Journal of Sport Communication, 3(4), 422-437. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsc.3.4.422
Wright, B. K., Williams, A. S., & Byon, K. K. (2017). Brand marketing via facebook: an investigation of the marketing mix, consumer-based brand equity, and purchase intention in the fitness industry. Marketing Management Journal, 27(2), 131-142. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/BRAND-MARKETING-VIA-FACEBOOK-%3A-AN-INVESTIGATION-OF-Wright-Williams/6fe4b07a55d97710eac529b8b7314c039b276569
Author notes
* Correspondence: Alejandro Lara-Bocanegra, alejandrolarboc@us.es
Additional information
Short title: Social Media in Fitness centers in Spain
How to cite this article: Valcarce-Torrente, M., Lara-Bocanegra, A., Bernal-García, A., & Pérez-Tur, F. (2024). Social Media in Fitness centers in Spain. Cultura, Ciencia y Deporte, 19(60), 2146. https://doi.org/10.12800/ccd.v19i60.2146





